GeoSeer Licensed Products Released
Posted on 2019-11-27We hinted at it in August and now it's here; today we're releasing a licensed version of the database that sits behind GeoSeer, creatively called: GeoSeer Licensed.
GeoSeer Licensed content allows organisations and businesses to host and integrate their own local copy of GeoSeer's industry leading database of spatial web services directly into their own applications, products, or services. We figure this can improve end-user workflows, make discovery of third-party data and services much easier, and help organisations realise some of vast economic benefits Open Data presents - estimated at €75 billion across the EU in 2020 alone. Also, you can build cool things with it.
This nicely compliments the GeoSeer API which was released back in April. Where the API allows organisations to easily build GeoSeer's search into web applications by making calls to our servers (like the GeoSeer WebGIS demo does), GeoSeer Licensed allows organisations to host the database locally, or release it in a product, meaning any sort of application can be built around it, not just search.
The Value Add
Lets be honest, there's nothing stopping you from building your own spider, finding 550+ dataportals to use as seeds, scraping half a million web-pages a month, and building your own database of geospatial web services. So why use GeoSeer Licensed?
- Industry Leading Database - At the time of writing we're not aware of any database of geospatial web services anywhere near as large as this (and we've looked).
- Current - We run regular crawls to make sure everything in GeoSeer Licensed is current. We provide monthly updates so you always have the latest data.
- Pre-Cleaned - despite these being standards, everyone likes to do things differently. We've pre-cleaned the fields and tried to standardise them to make them consistent. For example we've found no less than 55 ways to say
"No license fees"across 12 languages and turned that into a simple:"No". - XML Free - it's 2019 and fewer people want to deal with the hassle of namespaces, esoteric data models, and the other complexities XML brings. We've extracted the data from the XML documents and put it into a database, with some JSON sprinkled in where necessary.
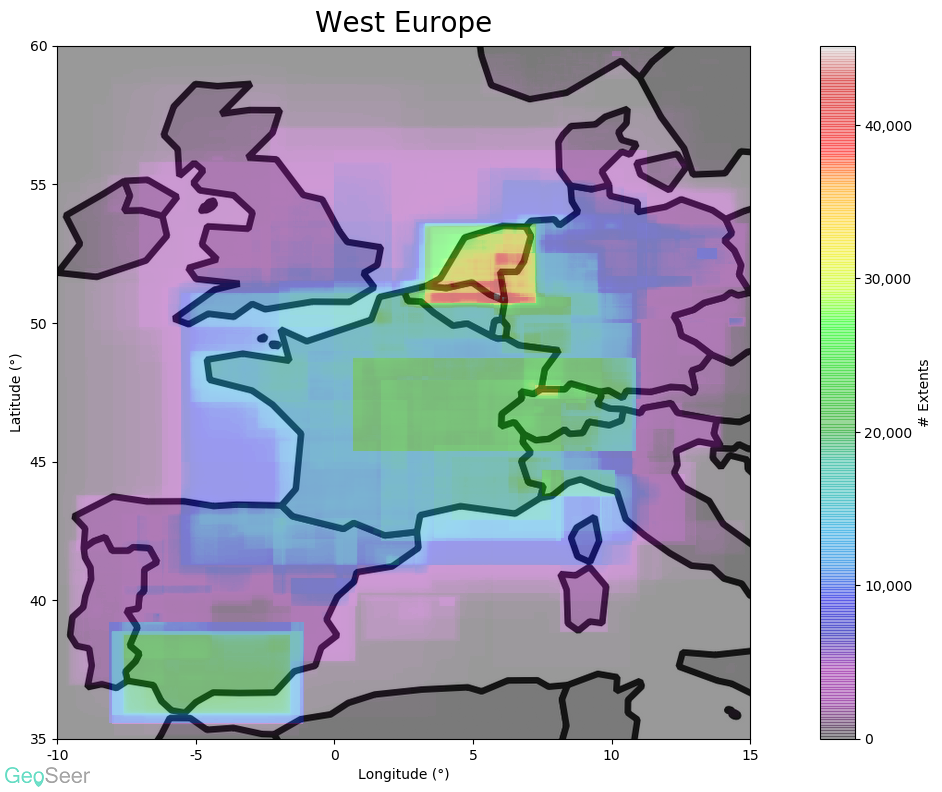
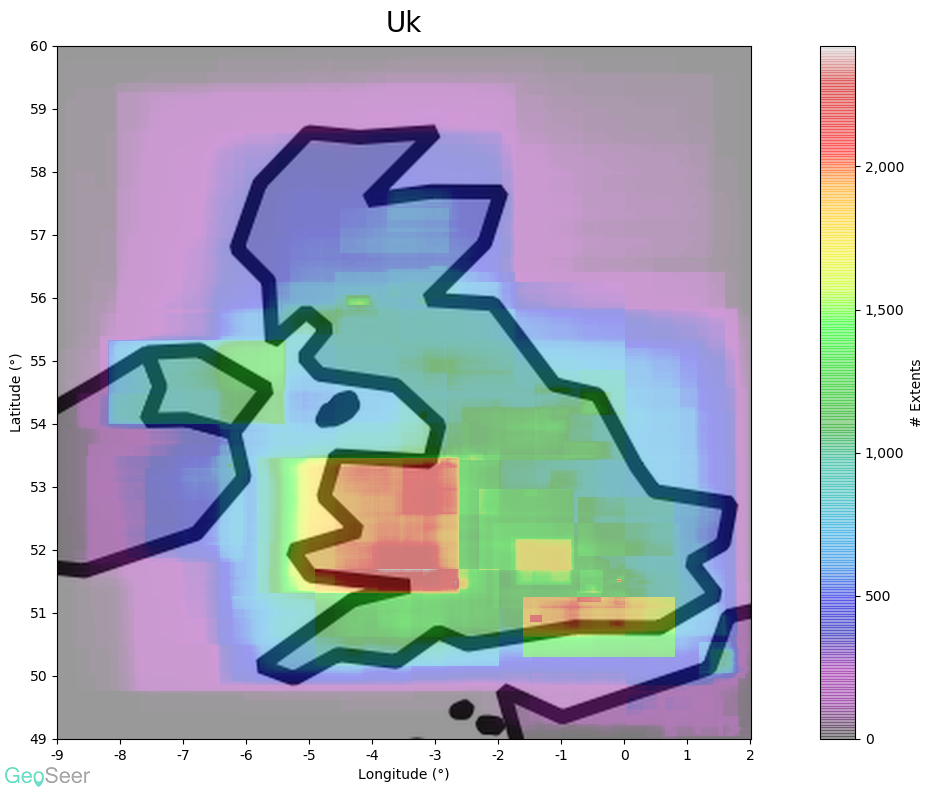
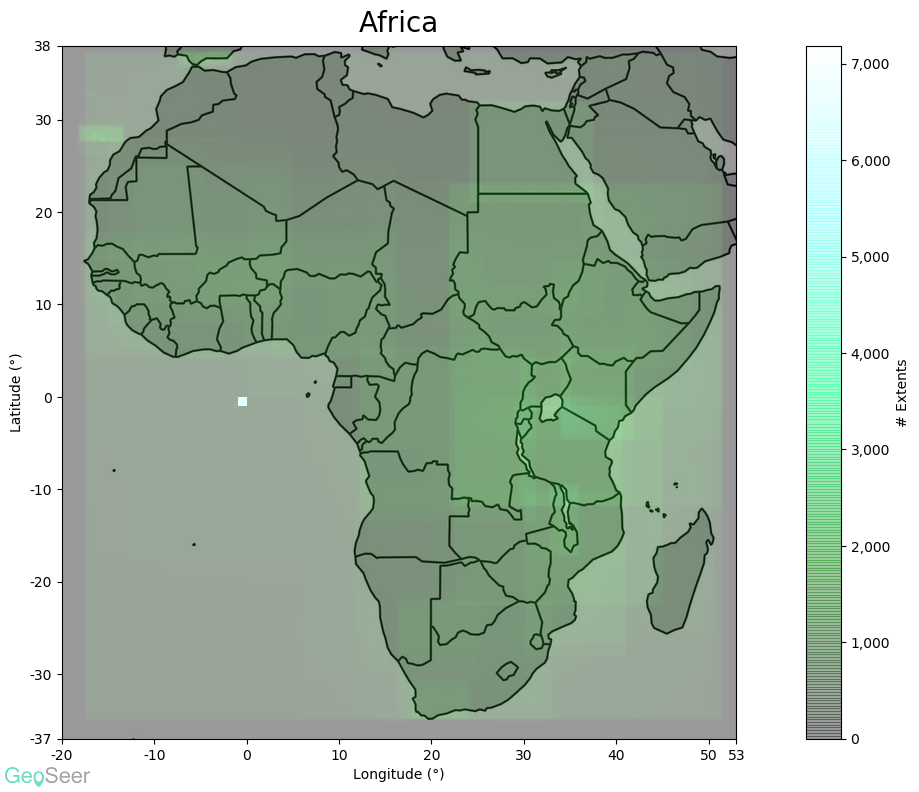
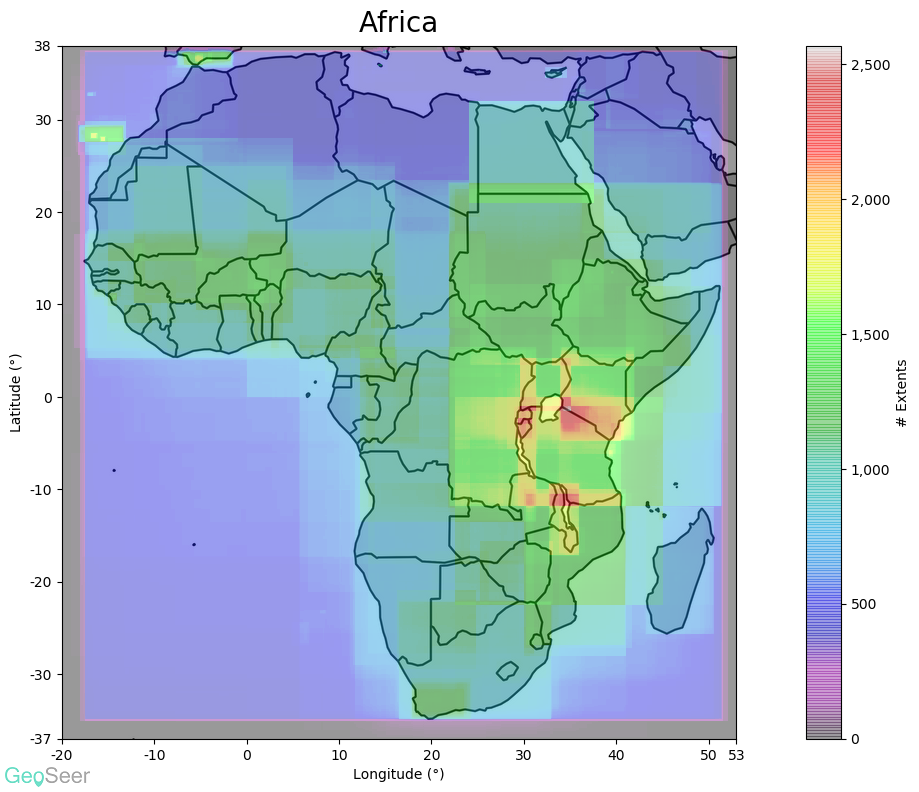
- Spatial Extents - For GeoSeer Datasets we include the extents bounding boxes in WGS84 format, along with scale-appropriate textual representations of the locations, potentially down to county level (like you see in GeoSeer Search).
- Quick start - Because we've done all the hard work, written up documentation about what each field means (so you don't have to read the standards), and packaged it in an SQLite database, it's super easy to get started with. Simply open your favourite database admin tool (it probably supports SQLite), and get querying with good old fashioned SQL.
The Products
GeoSeer Services is a database with all of the current geospatial web services that GeoSeer knows about in it, as well as information about their endpoints, hosts, and more. At the time of writing it has over 215,000 services in it from across 4,930 different hosts. This information is good for investigating who is hosting services, what sorts of services exist, INSPIRE deployment patterns/conformity, etc.
GeoSeer Datasets builds on GeoSeer Services, including not only all of the service information, but all of the dataset metadata as well. This includes: dataset extent bounding boxes, dataset keywords, declared projections, scale-appropriate textual location, metadata urls, and more. GeoSeer Datasets is well suited to building search engines (surprise!), GIS, web-GIS, academic research, and much more.
Both products are available with a number of different license types, from a research license through to commercial licenses. We can also provide subsets of the database if you don't want everything.
We like to think we've built a great search engine around this data, so now it's your turn - what can you build with it? Find out more about GeoSeer licensing.
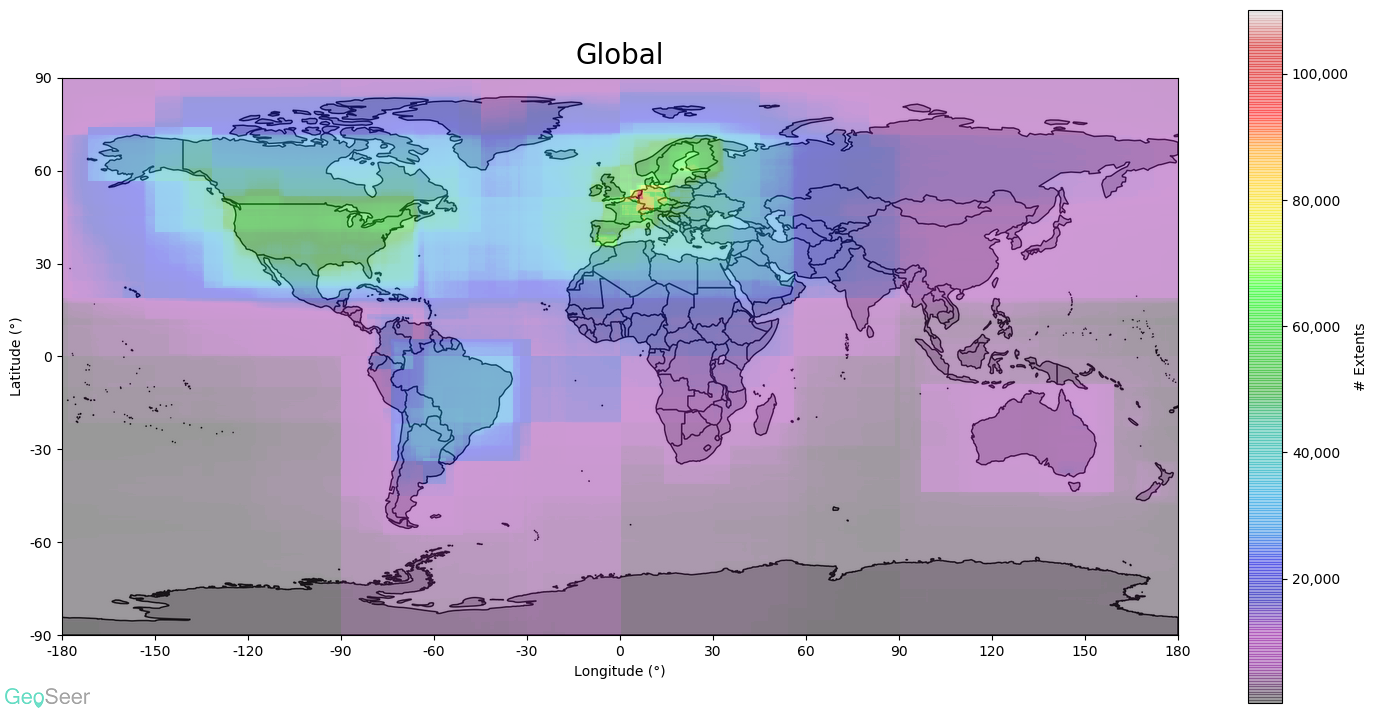 Starting with the global plot (above) it's obvious that the EU's INSPIRE directive has had a considerable effect, particularly in central Europe. The USA and Brazil also have considerable coverage.
Starting with the global plot (above) it's obvious that the EU's INSPIRE directive has had a considerable effect, particularly in central Europe. The USA and Brazil also have considerable coverage.